
Definitive or secondary nucleus : 2 Polar nuclei fuse in central cell – form diploid nucleus.ġ0. Antipodal cells : 3 cells at chalazal end.ĩ. Synergids with filiform apparatus – guides pollen tube towards egg.Ĩ.
Egg apparatus : 3 nuclei at micropylar end.ħ.

Microsporangium contains microspore mother cells (2n) which undergo meiosis to form microspore tetrad.Outer epidermis (Protective) followed by fibrous endothecium, thin walled middle layers and tapetum innermost nutritive layer. Anther wall is outer layer and microsporangium has sporogenous tissue.Mature anther has anther wall and microsporangium.Heterogeneity appears with formation of archesporial cell.Monothecous (Having single lobe) → Bisporangiate (Having two pollen sacs).Usually dithecous (Having two lobes) → tetrasporangiate (Having four pollen sacs).Gametes ← within flower ← Reduced structure ← gametophyte

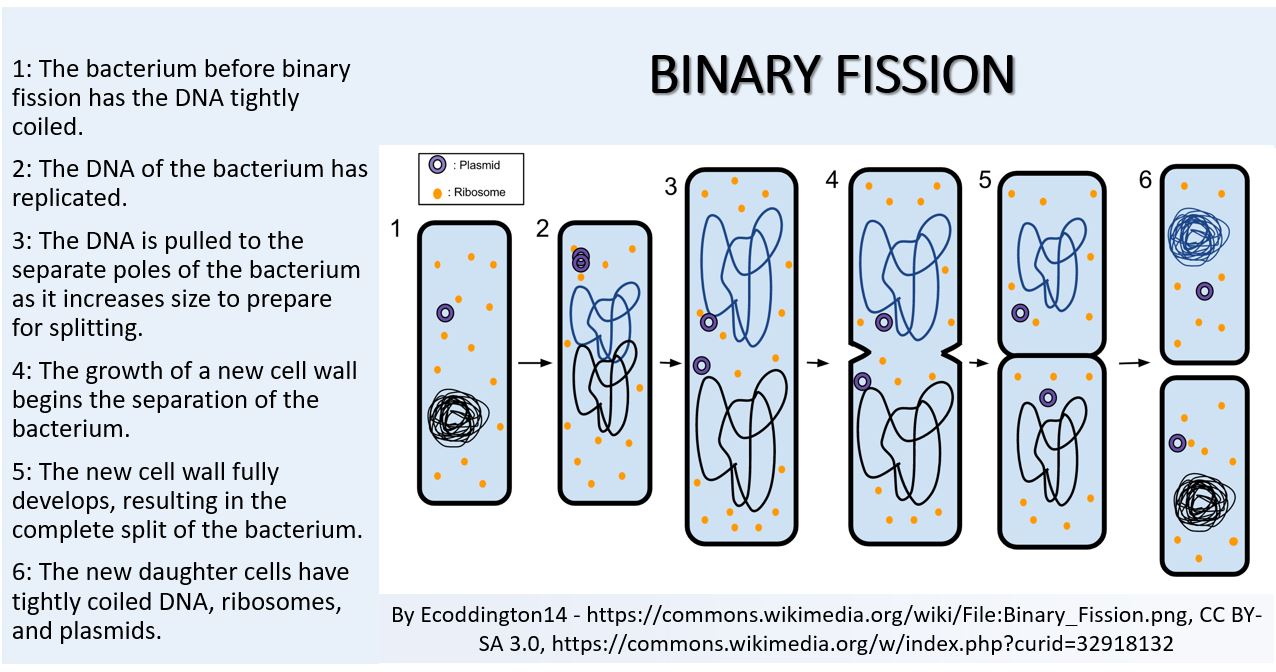
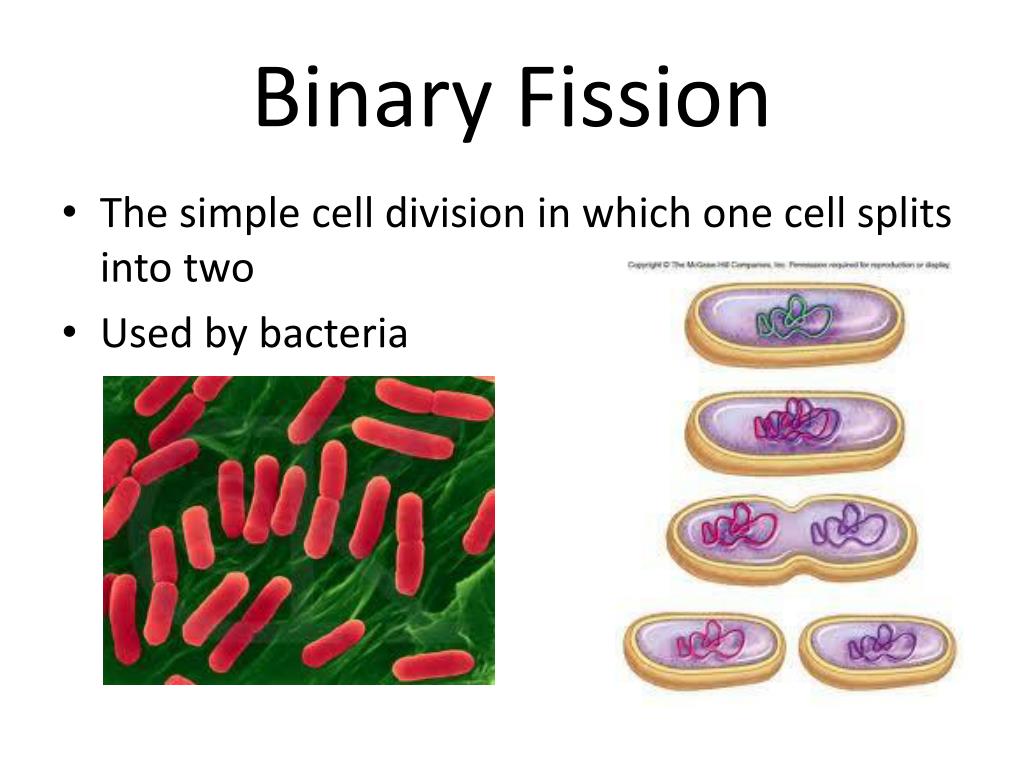
Diploid sporophyte is dominant plant body → Meiosis → Haploid spores → Sexual reproduction – Two major events –Ĩ. Flowers, specialized reproductive structure producing haploid gametes-ħ. Variations are useful for survival and evolution of species.Ħ. Production of genetically different offspring.ĥ. In higher plants, flowering indicates beginning of reproductive phase.Ĥ. Involves fusion of two compatible gametes (male and female).ģ. Micropropagation - Modern method to get plants from tissue culture.A small amount of plant tissue is carefully and aseptically grown to get plantlets.Joining of two plant parts stock and scion.New plants are identical to parent plant.Artificial methods useful in agriculture and horticulture.Reproduction with vegetative plant parts.Inheritance of genes of parent by progeny. Production of genetically identical progeny, i. Fusion of two compatible gametes or sex cell is not involved.Ģ. TWo types – Asexual reproduction and Sexual reproduction.ġ.To maintain continuity of life, organisms produce offspring showing similar characters.Essential Process related to continuity of species.Reproduction is production of young ones like parents.Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Notes Chapter 1 Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants By going through these Maharashtra State Board 12th Science Biology Notes Chapter 1 Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants students can recall all the concepts quickly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
